Any blog or webpage editor using WordPress knows that the secret of this CMS is mostly connected with its plugins. These are new functionalities that you can easily download and install in the editor to add a new characteristic. Being able to retouch SEO elements, filter spam, add comments, add JavaScript… These are all plugins.
Once you know this, the hardest thing to do is to decide what you want and which plugin is the best option to achieve it. There is a large WordPress repository where most developers post their plugins for the benefit of users. But there are a lot of plugins and some of them are extremely similar. A solution to this dilemma is portfolios which other users have created to group and score plugins. It’s an option to help you decide.
How to upload a plugin to the WordPress repository
If you develop plugins for WordPress, first you need to upload your extension to the editor’s repository. Your extension will then be downloaded and installed by content editors. To do this, follow these steps:
– Register at WordPress Extend. WordPress provides a registration form. Developers need to enter their details such as name and surname, email address, location, webpage and interests. Only the first two are mandatory.
– After you have registered and submitted the form, you can log in and go to the plugin upload area. This step also includes a form; in this case, you need to enter information about the extension you wish to upload to the WordPress repository. The final URL for the plugin’s location will depend on the extension’s name. For example, the address for the well-known plugin Jetpack by WordPress would be: https://wordpress.org/plugins/jetpack/https://wordpress.org/plugins/jetpack/
– Always upload the plugin to the repository with a link to a .zip file.
– If the extension is approved, WordPress sends a confirmation email. You can find some of the conditions for obtaining approval on the FAQs page of the WordPress repository.
– Subversion is used for the final upload of the new functionality. Subversion is a completely free, open-source version control system which works with command line. It’s Linux based.
– There are three types of folders in the WordPress repository: trunks, tag and branches. The first folder is where the plugin must be installed. The second folder is where the extension is updated with successive versions; plugins in WordPress always require updates which adapt to the evolution of both the editor and its users. The last folder is used for testing.
The WordPress plugins with the highest number of downloads
Some extensions in the WordPress repository stand out for the number of downloads and comments among editors. This is the list of plugins with the most downloads in the collection:
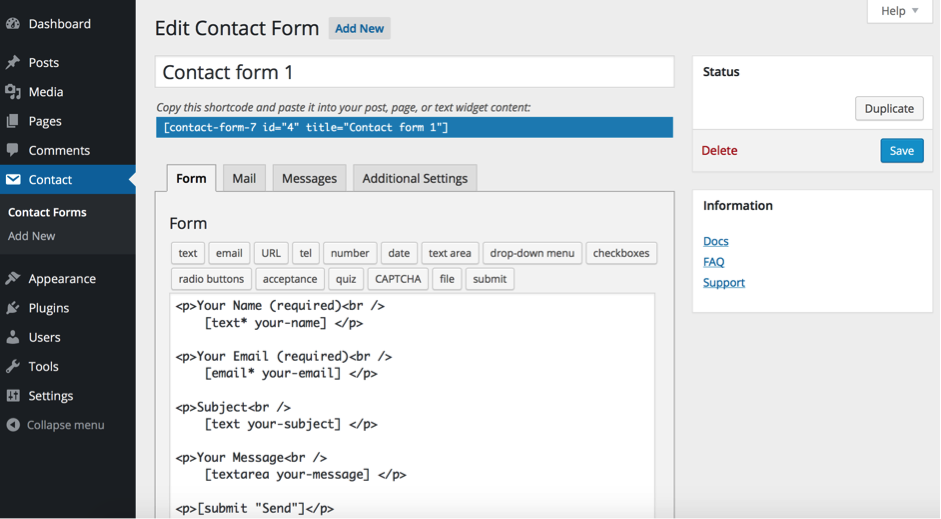
– Contact Form 7: extension for implementing contact forms in a blog or webpage. You can customize the forms’ content and style. You can create a registration form, a form to sign up for a newsletter, a form to sign up for a mailing list… It coexists with other extensions for CAPTCHA or spam filtering such as Akismet.
– Jetpack by WordPress: you could say this is a plugin of plugins. Jetpack facilitates statistics, security services, image optimization functionalities to lighten the page and reduce load times, save on hosting and band width… A lot of websites use Jetpack as a plugin.
– NextGen Gallery: the gallery system with the most downloads in WordPress. According to its repository page, this extension has exceeded 13 million downloads. Users can create photo galleries from images uploaded in batches; they can also import metadata (essential for SEO), use thumbnails, and reorder photos to create albums, etc. Additionally, this extension adds features for sizes, styles, transitions and light effects.

– W3 Total Caché: this plugin was designed with the express purpose of improving WPO (Web Performance Optimization). Its aim is to offer a better user experience. This is mostly achieved by reducing webpage load times by means of a cache. This improves server performance.
– Really Simple Captcha: this plugin was created to work with other extensions such as Contact Form. It allows you to add CAPTCHAS to registration or login processes in websites developed using PHP. The plugin works with two types of files: one where the CAPTCHA image is stored, and another where the answer’s text is saved.
Curated lists of WordPress plugins
The extensions of this CMS have given rise to a series of plugins categorization repositories. Their purpose is to help the editor’s users to choose the best plugin for them depending on the type of content and pages:
– WP Plugin Directory: this directory is organized by major categories and subcategories depending on the type of plugin. Social, mobile, photos, SEO, audio and video, comments, community, email management, development, advertising, e-commerce, security, languages… There are a lot of them.
– RankWP: this directory classifies WordPress plugins, and contains information about the daily download volume and number of installations. It’s not particularly visual and it doesn’t offer a great user experience but it can be pretty useful.
– Tidy Repo: this repository has a modern, card-type design where you can access the reviews section of the site. For example, it contains analyses of all plugins aimed at improving a website’s SEO. In these reviews, the team at Tidy Repo explains what each extension does, how it is installed, how each plugin should be used, and includes links you to the developer’s documentation for each functionality, etc. It’s very comprehensive.
– The Periodic Table of WordPress Plugins: this is an interesting approach to WordPress extensions; the typical periodic table has been adapted to the extensions. The plugins are chosen because of their popularity – the number of active installations on websites.
Follow us on @BBVAAPIMarket





























