Chatbots have become the next big thing in terms of innovation in the field of technology and information. Most instant messaging applications have incorporated facilities to launch chatbots on their platforms, whether for content distribution, customer service or e-commerce. In this respect, some startups are doing business by offering services for creating bots in a few steps without programming. An open door for nontechnical users.
One of these platforms is Chatfuel, which is possibly one of the most used in the market, but for now it’s more a field of exploration than a business. The idea behind this company is that any user can create a chatbot, with some level of artificial intelligence, to generate conversations with users in applications such as Facebook Messenger or Telegram, and soon in others such as WhatsApp, Kik, Viber or other services or communication tools between users such as the well-known Slack. The reality is that many of them use bots as a vehicle to gain users over rivals or get closer to the developer community.
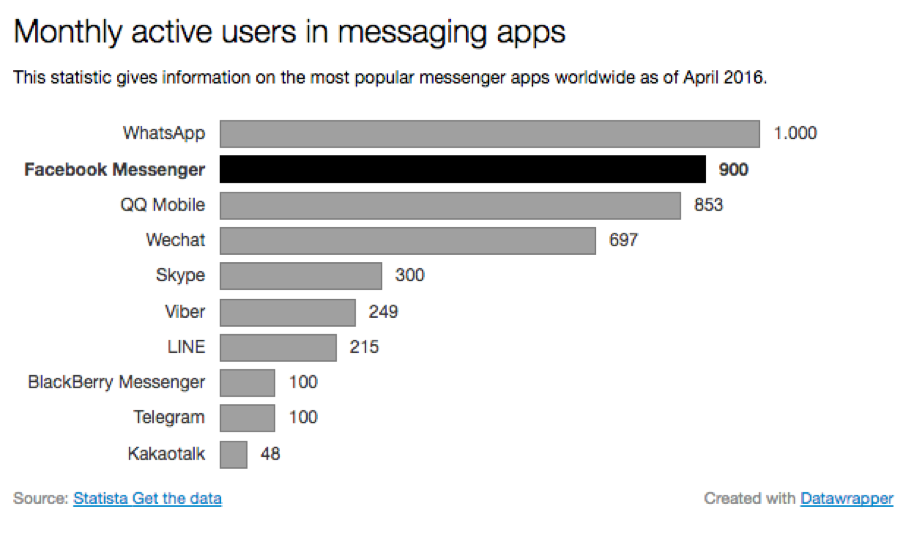
Today, as with almost everything that surrounds the smartphone, Facebook is the big player. Not only through Facebook Messenger, a messaging application with which Mark Zuckerberg’s company has high hopes, but also through WhatsApp, star of the sector and company acquired by the Menlo Park firm in 2014. This graphic by Statista shows the volume of monthly active users of the messaging app. The growth of Facebook Messenger is really astounding.
Bots in chat applications are trendy
The chatbot boom is a logical and natural trend within the smartphone ecosystem: more and more users, especially younger ones, are spending a lot of their time using mobile applications, with a great capacity to adapt to changes and technological developments. Forty-nine percent of smartphone users between 18 and 29 years old use messaging apps; in the case of WhatsApp, they use the app 200 minutes a week on average, with nearly 7 trillion messages in 2015; Facebook Messenger, users and businesses share almost 1 billion messages each month.
One of the great advantages shown by conversational chatbots for users is the accessibility of services in the correct space and time, and how each of them can return to the service consumed in the past in a user-friendly interface. Robots allow push notification systems and in-app messages that provide value to the user. The idea is an app can provide many simultaneous services in a single interface.
That’s what Chatfuel is like, the platform for creating bots
Chatfuel is possibly the most ambitious project concerning a platform for creating simple bots, on Facebook Messenger and Telegram for now, although its founders want to expand to other messaging applications. The platform was launched in 2015 by Russian developers Dmitry Dumik and Artem Ptashnik with funding from Yandex and based on the original Paquetbot. Chatfuel is not only comfortable for novice users, it’s also free. All that is necessary is to be somewhat bold and open an account in Chatfuel. Media such as Forbes and TechCrunch have relied on them for their chatbots.
The steps required to create a bot in Chatfuel for Facebook Messenger are as follows:
● Chatfuel has a bot tutorial from which users can start developing their own product with additional help, not from scratch. It’s as simple as selecting the option to create a bot in Facebook Messenger, then choosing a name for the bot (it can be changed later), choosing Bot Tutorial as a template and selecting create a bot.
● The initial interface to begin programming the different conversational paths with future users would be something like this:
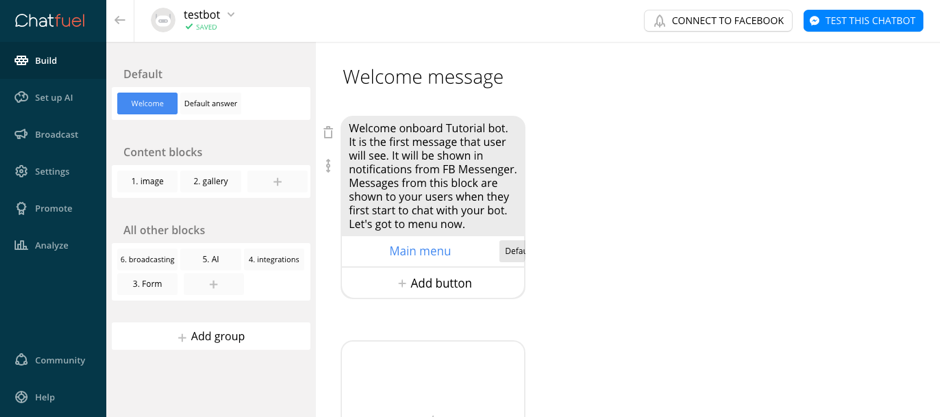
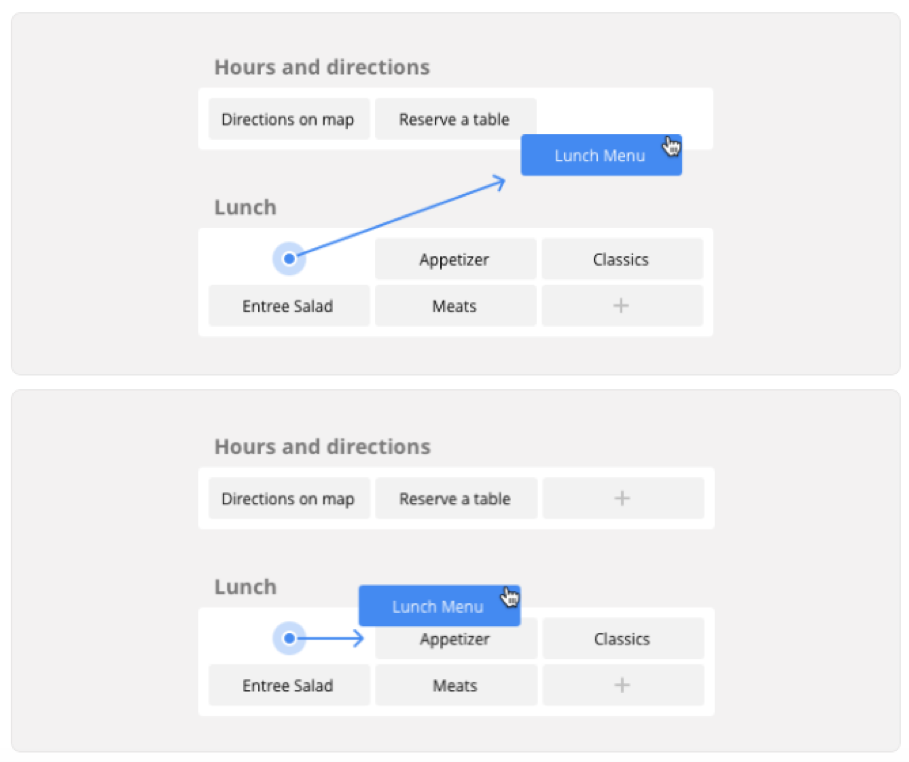
On the left Chatfuel customers have a menu with a field called Build for programming the bot, Setting to change the product configuration items and another as Analyze where the different metrics on the bot are accumulated: activity and retention of users and levels of popularity of the buttons and the menus of the bot itself.
● In addition, Chatfuel has a field (Set up AI) which can be very useful for giving the conversational bot human details. The level of artificial intelligence that can be introduced into the application is reduced, but it adds value: in the end it is based on a system of keywords and the creation of automatic responses from them. The user chooses a language (more than 50 are available: English, Spanish, French, Italian, German and even Latin), enters a word or phrase and generates a response to that particular sequence. And it really works effectively.
● You can test the bot within Facebook Messenger and it can also be made public by connecting it with the messaging platform. Access to test features and publishing are in the upper right part of the initial interface.

How to create conversations in Chatfuel
Bot programming, i.e. how the structure and messages that will be distributed through the platform, in this case Facebook Messenger, are created is quite simple and flexible. Chatfuel provides a tutorial where key elements are explained for users: cards, blocks and groups.
● Blocks: this is what Chatfuel calls each of the basic components of a bot. Each block is composed of one or more cards, each with a message (with a maximum of 320 characters, three different fields for the menu and the possibility of introducing photo galleries, YouTube videos or GIF format images). In addition, each of these blocks can be linked with others: a new block is created, then a button is generated in an existing one, the button is filled and then the name of the block that was created earlier that you want to link to the existing one is selected. When the button is clicked, the input of the entire linked block is triggered.
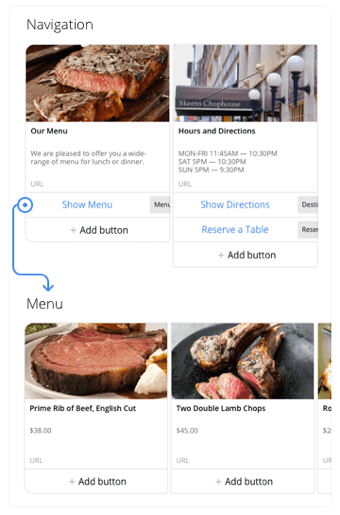
Among the existing blocks there are two types that are really important: the welcome message and the default answer. The first will always be displayed to all new users that add the bot to their contacts in Facebook Messenger. The default answer is what allows the conversation with the user to not end when there is a response that has not been envisaged: for example, sends a word or phrase not foreseen in the artificial intelligence field and it is necessary to have a kind of response that fulfills the objective of continuing the conversation.
● Groups: the creator can use groups to arrange the blocks of the bot and generate some conversational structure. It’s possible to move blocks between groups, you can move the blocks within each group or create, delete and rename blocks, except the default group.